Human Anatomy and Physiology 10 Chapter 8 Joints Review Sheet Answer Key
About Human Torso
If we were to "suspension autonomously" the man torso at the microscopic level, then the prison cell would plant its most basic unit.
The average adult has somewhere betwixt 30 – 40 trillion cells, and an estimated 242 billion new cells are produced every twenty-four hour period. When a select group of cells with similar functions come together, it forms a tissue.
Tissues cumulate into organs, group of organs form organ systems and somewhen, a complete organism.
Cells -> Tissues -> Organs -> Organ System -> Organism
- Human Anatomy
- Homo Physiology
- Circulatory System
- Digestive System
- Reproductive Organization
- Respiratory System
- Nervous Arrangement
- Primal Points About the Human Body
Human Anatomy
Skeleton
The human body exhibits a diversity of movements from walking and running to itch, jumping and climbing. The framework that enables united states to do all these activities is the skeleton. Humans have equally much as 300 bones at birth. However, the bones start to fuse with age. At adulthood, the total number of bones is reduced to 206.
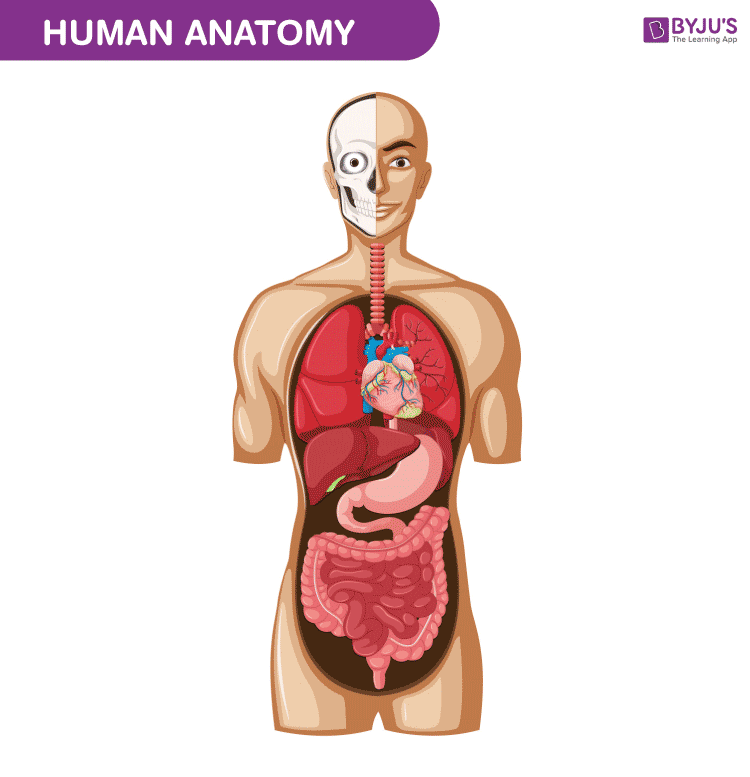
Human Anatomy is the scientific written report of form and shapes of human being beings
The skeleton likewise protects several vital organs such as the heart, lungs and the liver. Bones are attached to other bones through ligaments, a fibrous connective tissue.
Joints are the points at which two or more bones come across. They enable a range of movements like rotation, abduction, adduction, protraction, retraction and more. Based on flexibility and mobility, joints tin can be further classified into movable joints and immovable joints. Movable joints are flexible while immovable joints (likewise called fixed joints) are non-flexible since the bones are fused.
Muscles
Muscles are specialised tissues which assist the basic in locomotion. Muscles are attached to the basic through tendons. Motility of limbs happens due to the contraction and relaxation of the respective muscles nowadays in that region. Joints assistance in the flexibility of bones, but a bone cannot be aptitude or stretched until a muscle acts on it. In other words, the muscles attached to that os pulls information technology to the management of move.
Furthermore, nearly motion involves muscles that work as a pair. For example, when we curve our arm, muscles in that region contract, become shorter and stiffer and pull the bones to the direction of movement. For relaxation (stretching), muscles in the opposite direction accept to pull the bones towards it.
Also Read: What is Liver
Listing of Human Torso Parts
- Human trunk parts comprise a head, neck and four limbs that are connected to a trunk.
- Giving the trunk its shape is the skeleton, which is composed of cartilage and bone.
- Man body internal parts such as the lungs, middle, and brain, are enclosed within the skeletal system and are housed within the different internal body cavities.
- The spinal string connects the encephalon with the residue of the body.
Human Trunk Structure
There are different cavities in the human torso that house diverse organ systems.
- The cranial crenel is the space inside the skull, it protects the encephalon and other parts of the central nervous system.
- The lungs are protected in the pleural cavity.
- The abdominal crenel houses the intestines, liver and spleen.
Humans have evolved separately from other animals, but since nosotros share a distant common antecedent, we mostly have a body program that is similar to other organisms, with just the muscles and bones in different proportions.
For example, we might assume giraffes have more vertebrae in its neck than humans. No, despite existence incredibly tall, giraffes take the same number of vertebrae, i.e. they also have seven vertebrae in their neck.
One of the virtually prominent characteristic features is the power to employ our hands, especially for tasks that require dexterity, such as writing, opening a canteen of h2o, opening a doorknob, etc.
This is the result of humans having ancestors that began walking on their hind limbs rather than using all iv limbs. Near of our anatomical insight was gained through the dissection of corpses (cadavers), and for a long fourth dimension, it was the only manner we could gain anatomical knowledge about the homo body. It was a rather grotesque affair, merely information technology fabricated upwardly the majority of medical literature for centuries. These days, technological innovation has fabricated it possible to explore human beefcake at a microscopic level.
Even to this mean solar day, scientists are newly discovering organs that were previously overlooked or have been mistakenly identified as other existing tissues. In 2018, scientists had discovered a new, body-wide organ called the Interstitium that exists correct under the pare.
Human Physiology
It is referred to the concrete, mechanical, and biochemical role of humans. This connects health, medicine, and science in a style that studies how the human torso acquaints itself to physical activity, stress, and diseases.
The person who is trained to written report man physiology is called a physiologist. Claude Bernard is referred to as the father of Physiology for his exemplary research.
Read More: Physiology
Human Body Parts and their Functions
The list of human trunk parts vary as the standard definition of an organ is all the same upward for fence. Withal, at that place are an estimated 79 organs identified to date. We also possess organs that have "lost" their function throughout our evolution. Such organs are called vestigial organs.
Some of these organs work together and form systems that are specialised to perform a specific function or a set of functions. Collectively, these are known as organ systems.
And out of these 79 organs, v are crucial for survival, and any damage to these five organs might result in termination of life. These five crucial human body parts are the brain, heart, liver, lungs and kidneys. Read on to explore more near these body parts and their functions in detail:
Circulatory Organization
The circulatory arrangement is besides referred to equally the cardiovascular organization. It comprises the heart and all the blood vessels: arteries, capillaries, and veins. In that location are substantially ii components of circulation, namely:
- Systemic circulation
- Pulmonary circulation
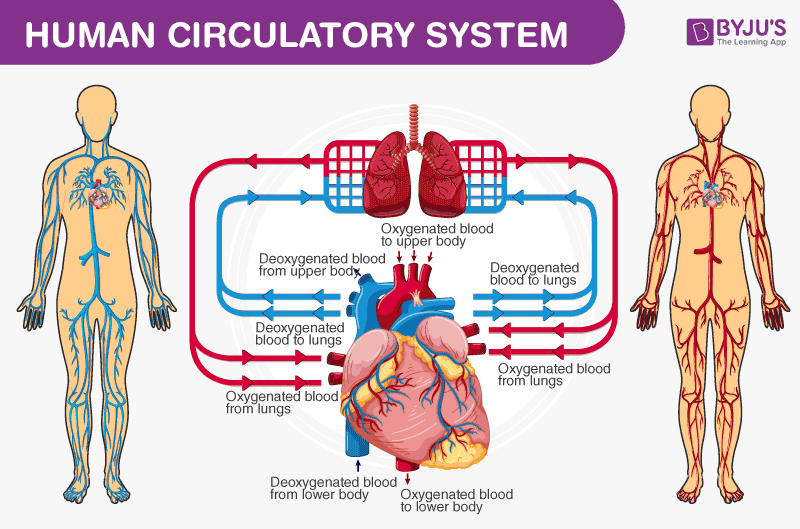
Diagram showing pulmonary (blue) and systemic circulation (ruby)
Besides these 2, there is a third type of apportionment called Coronary circulation. Because claret is the body'south connective tissue, it helps to transport essential nutrients and minerals to the cells and waste byproducts away from it.
Hence, information technology is besides known every bit the torso'due south "transport system." Anatomically, the homo heart is similar to other vertebrate hearts in the animate being kingdom and hence, is a homologous organ.
Likewise Read: Double Apportionment
Digestive Organisation
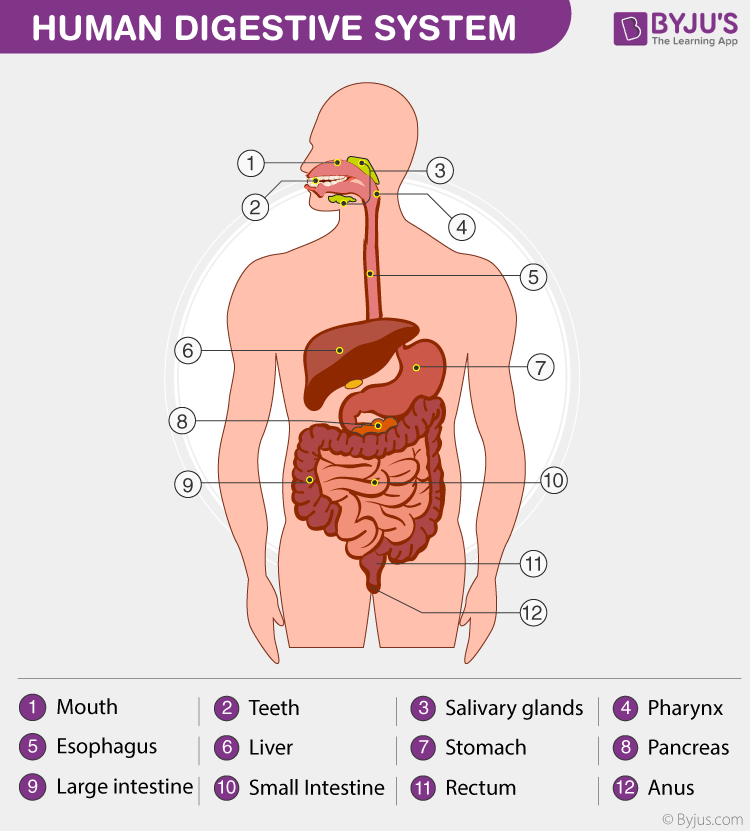
A diagram of the homo digestive system detailing diverse components
The digestive system breaks down food and assimilates nutrients into the body, which the body and so uses for growth and cell repair.
The major components of the digestive system are:
- Mouth
- Teeth
- Natural language
- Oesophagus
- Breadbasket
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Minor and big intestines
- Rectum
The process of digestion starts with mastication (chewing food). Then, the saliva mixes with food and forms a bolus, a small rounded mass that can be easily swallowed. One time swallowed, the food travels down the oesophagus and into the stomach. The stomach secretes strong acids and powerful enzymes that break the food downwardly into a paste.
Information technology and so moves into the small intestine where the food is broken down fifty-fifty more considering of the bile secreted by the liver and powerful, digestive enzymes from the pancreas. This is the stage at which nutrients are captivated from the food.
The leftover materials (stool) and so move on to the large intestine where it transforms from liquid to solid, as h2o is removed. Finally, information technology gets pushed into the rectum, ready to be eliminated from the trunk.
Explore: The Structure and Role of the Gastrointestinal tract
Reproductive System
The human reproductive system is too known equally the genital system that comprises internal and external organs that help in reproduction. It varies for both males and females. Hormones, fluids, and pheromones are all connective accessories for the reproductive organs to function.
Female Reproductive Organization
The female reproductive organization consists of the post-obit:
- Ovaries: Produces ovum – female egg as well as the hormone estrogen.
- Uterine tubes: Oviducts or fallopian tubes are the other names given for uterus tubes.
Too known as the womb, the uterus is a pear-shaped organ where the fetus grows. The neck is the road to the vagina and gateway for sperm to enter. Vagina acts as the route for a penis to enter during intercourse and the exit of the fetus during delivery.

Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive organisation consists of testicles, which act every bit a storehouse for sperms. These oval-shaped organs, are encased in a pouch that is called scrotum.

Next to the testis is the vas deferens that are the accessory ducts for the male sexual organisation. When sperm is formed, it is mixed with fluids that are produced by seminal glands, prostate gland, and Cowper's gland. The master purpose of Cowper gland is to hike the semen volume and lubrication during coitus.
More to Explore: Reproductive Arrangement
Respiratory Arrangement
The respiratory process involves the intake of oxygen, and the breathe of carbon dioxide from the body. This system is likewise known as the ventilatory system, gas exchange system or respiratory apparatus. Vertebrates like human beings possess lungs for respiration. The process of respiration starts with the bike of inhalation and exhalation.
Inhalation results in the oxygen entering into the body and exhalation results in carbon dioxide exiting from the trunk. Anatomically, the respiratory arrangement comprises the post-obit organs:
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Lungs
- Diaphragm

A diagram of the human respiratory system highlighting the gas exchange procedure
Past diffusion, molecules of carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged passively among the blood cells and external surroundings. This swap is washed through alveoli (which are the air sacs) in the lungs.
More than About: Respiratory System
Nervous System
The voluntary and involuntary deportment are maintained and taken care of past the central nervous system. Information technology helps to channel the signals to and from different parts of our torso. Nervous System is broadly classified into 2 categories:
- Central Nervous Arrangement
- Peripheral Nervous Organization
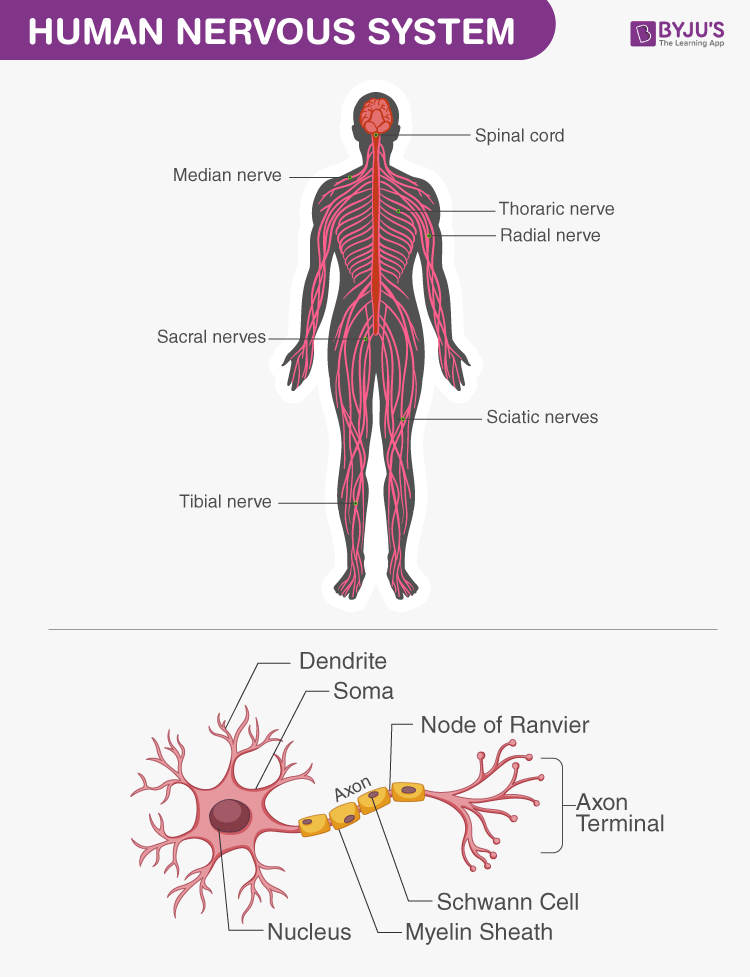
Distribution of Fretfulness in humans (top) and the Neuron (lesser)
The central nervous arrangement contains the brain and the spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system includes fretfulness and ganglia that are present outside the brain and spinal cord. Through the axons, every office of the body gets connected.
Primal Nervous System consists of:
- Forebrain: It comprises the cerebrum, hypothalamus, and thalamus. The largest function of the brain is the cerebrum. Thinking, perceiving, controlling motor part, receiving and processing data and understanding linguistic communication are the main functions done past this section of the encephalon. Also, sexual development and emotion functions are fastened to the fore-brain.
- Midbrain: It is situated between the hypothalamus and thalamus. The brain stem is associated with the midbrain. Auditory and visual responses are controlled by the mid-encephalon.
- Hindbrain: The medulla, pons, and cerebellum are together, tied in the hind-brain. Interconnections of different parts of the brain's surface that helps to accommodate neurons and connect them to the spinal column are done by the Hind brain.
Peripheral Nervous Arrangement consists of:
- Somatic nervous system: The organization's main purpose is to transmit the motor and sensory impulses from CNS and back. It is linked to all the sensory organs, limbs and skeletal system. Imagine a scenario where you are riding a bicycle, and all of a sudden, you spot an obstacle (say a dog) on the route. Your ability to immediately swerve out of the obstacle's path and avoid the crash is the effect of the somatic nervous arrangement taking activeness.
- Autonomic Nervous Arrangement: This arrangement works without the person's effort. The system helps to relay impulse from the central nervous system to smooth muscles and involuntary organs such as your heart, lungs etc. As well, it prepares the body against whatsoever violent attacks or aberrant conditions such every bit high torso temperature during a fever or high rate of animate and blood pressure after a strenuous exercise.
Further Reading: Nervous Organization
Key Points About the Human Body
Every human existence, tissues, human being body parts and the organ systems are made upward of cells- the fundamental unit of life. Anatomy is the scientific discipline of understanding the structure and the parts of living organisms. Physiology, on the other hand, deals with the internal mechanisms and the processes that work towards sustaining life.
These can include biochemical and physical interactions between various factors and components in our body. With the progress of development, organisms began to exhibit avant-garde characteristics and features that enabled them to be more efficient and thrive in their respective surround.
The human structure can exist described every bit bipedal, with hair covering the trunk, presence of mammary glands and a set of extremely well-adult sense organs. With respect to human body anatomy, we have a specialized circulatory system that enables the efficient transport of materials and nutrients within the torso.
The presence of a well-developed digestive system helps to extract essential nutrients and minerals required by the body. A well adult respiratory arrangement ensures the efficient gas exchange and the nervous system enables coordination and interaction within the body and also the external environment, thereby ensuring survival.
Frequently Asked Questions on Human Anatomy And Physiology
What do y'all hateful by human anatomy?
Anatomy is the study of the structure of an object. Human anatomy deals with the style the parts of humans interact to form a functional unit of measurement.
What do you understand by human physiology?
Man Physiology deals with the mechanical, biochemical and concrete functions of humans. It serves as the foundation of modern medicine. It is the study of the functioning of homo organs.
Who is the father of human physiology?
Claude Bernard is the father of human Physiology. He is too referred to as the father of mod experimental Physiology.
What is the importance of human physiology?
Human being physiology lays the foundation upon which our knowledge of life is built. Information technology helps us to know how to treat diseases and how to manage stress laid upon us by unlike environments.
Who is the father of human beefcake?
Andreas Vesalius is known as the male parent of human beefcake. He was Belgian born in the family of physicians. His most famous work, Fabrica of Andreas Vesalius won peachy recognition.
What are the unlike types of beefcake?
At that place are two unlike types of anatomy- gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy deals with things that tin exist seen with the naked optics, whereas microscopic beefcake deals with the things that tin only be viewed under a microscope.
How is human anatomy relevant?
Human anatomy helps us to empathize the structure and relationship of all parts of the torso. It as well helps us to know the characteristics of different trunk parts.
How are anatomy and physiology different from each other?
Beefcake helps us to know about the structure of the dissimilar trunk parts while physiology studies the functions and relationships of body parts.
What are the of import organs of the homo body?
The important organs of the body include- brain, lungs, heart, kidney, liver, stomach, intestines, float.
What are the dissimilar systems of our body?
The different systems of our body include- cardiovascular system, endocrine system, digestive system, respiratory arrangement, excretory system, lymphatic system, nervous system, muscular system, and skeletal system.
For more data about human body, human body parts, or any other related topic, please visit BYJU'S Biological science.
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/human-body-anatomy/
0 Response to "Human Anatomy and Physiology 10 Chapter 8 Joints Review Sheet Answer Key"
Post a Comment